Introduction to Mica
Mica is a generic term applied to a group of Complex aluminosilicate minerals having a sheet or plate like structure with different composition and physical properties. All mica form flat six-sided mono clinical crystals with a remarkable cleavage in the direction of large surfaces, which permits them to easily split into optically flat films. When split into thin films, they remain tough and elastic even at high temperature. Mica possesses some of the most outstanding combinations of chemical, physical, electrical, thermal and mechanical properties which are not found in any other product.
Typical End uses of natural sheet mica :
·
Electrical Apparatus
·
Electric Heating Appliances
·
Electrical Control
·
Electrical Lighting Equipment
·
Industrial Electric Heating Appliances
·
Mechanical Uses
·
Miscellaneous Electrical Uses
·
Radio, Radar, Television etc.
·
Motors and Generators
·
Transformers
WE DEAL IN BOTH MUSCOVITE AND PHOLGOPHITE MICA
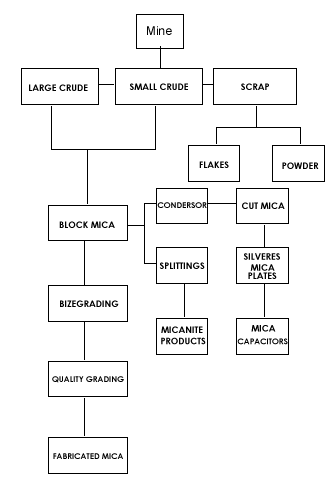
MICA PROCESS FLOW CHART
Chemical Properties Muscovite Mica :-
|
1 |
Silica (SiO2) |
45.57% |
|
2 |
Alumina (Al2O3) |
33.10% |
|
3 |
Potassium Oxide (K2O) |
9.87% |
|
4 |
Ferric Oxide (Fe2O3) |
2.48% |
|
5 |
Sodium Oxide (Na2O) |
0.62% |
|
6 |
Titanium Oxide (TiO2) |
Traces |
|
7 |
Calcium Oxide (CaO) |
0.21% |
|
8 |
Magnesia (MgO) |
0.38% |
|
9 |
Moisture at 100° C |
0.25% |
|
10 |
Phosphorus (P) |
0.03% |
|
11 |
Sulphur (S) |
0.01% |
|
12 |
Graphitic Carbon (C) |
0.44% |
|
13 |
Loss on ignition (H2O) |
2.74% |